Pancreatic Disorders
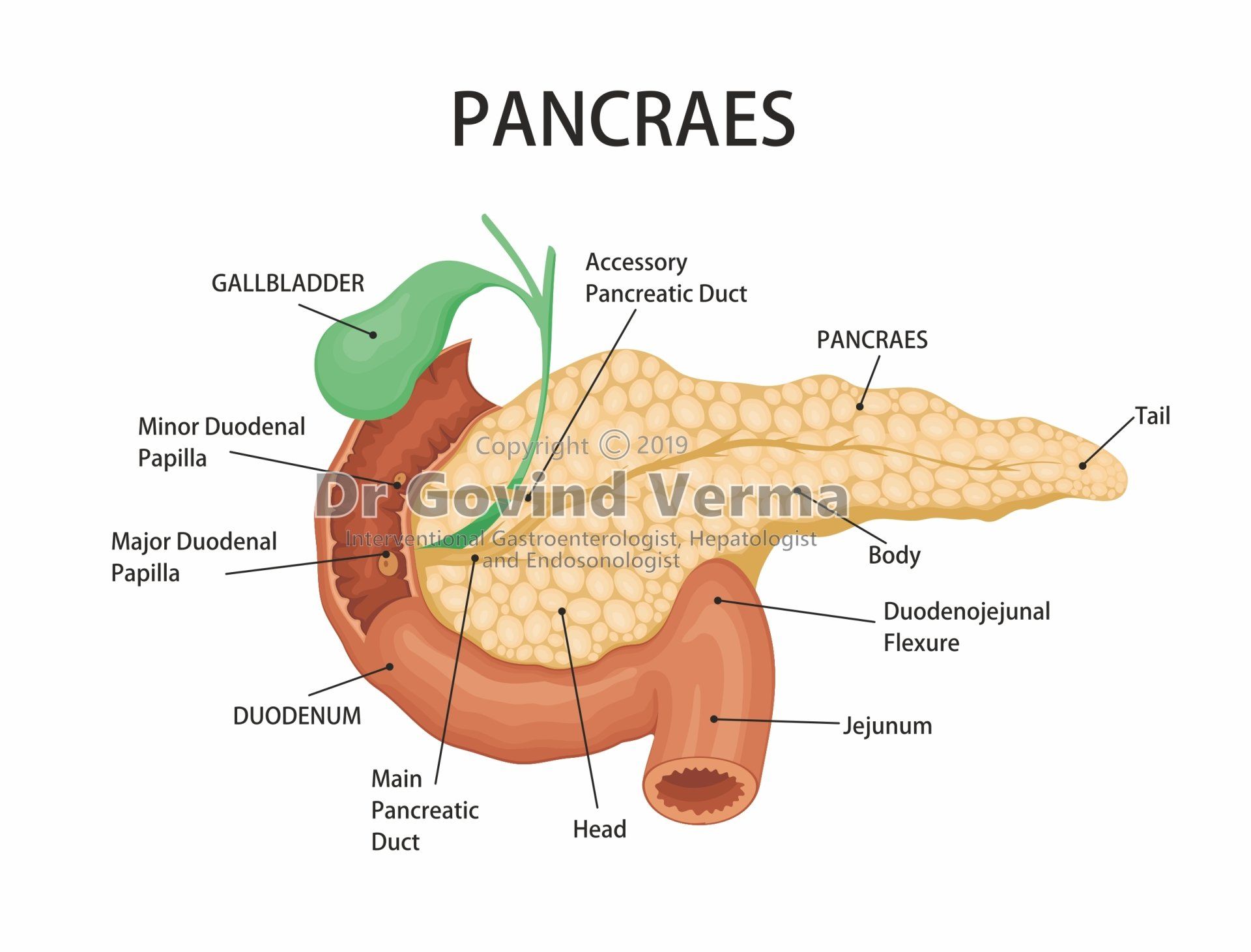
The pancreas is a flat, narrow gland about 6 to 8 inches long; located inside abdominal cavity, behind the stomach and below the liver. It has three sections ie head, middle, and tail. Its head section connects to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
Common bile duct also goes through the head section of pancreas, carrying bile from liver and gallbladder into small intestine. The bile duct and pancreatic duct usually connect together before entering the duodenum and share a common opening into small intestine.
Pancreas functions
The pancreas performs different functions that are most important for human body.
Endocrine function: it produces hormones, including insulin and glucagon, and releases them into the blood. These hormones regulate sugar (glucose) transport into the body's cells, where it is used for energy and to help maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Exocrine function: It releases powerful enzymes to break down and digest foods, fats, proteins, and carbohydrates in our small intestine. The enzymes normally are produced and carried in an inactive form to the small intestine, where the enzymes are activated as needed. It also makes and releases bicarbonate that neutralizes stomach acids and allows for the activation of pancreatic enzymes.
What is Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis can start suddenly and stay last for many days, its difficult to find in early stages. Pancreatitis occurs when its digestive juices, or enzymes become activated inside pancreas and start damaging pancreas; which causing irritation and injury to pancreas tissues and leading to inflammation.
Pancreatitis have severe complications, that require immediate attention:
- Pancreas infection
- Diabetes because of insulin mismanagement
- Kidney problem / failure
- Malnutrition due to lack of digestive enzymes
- Fatigue and dehydration due to diarrhea
- Pancreatic cancer
- Necrotizing pancreatitis , tissues die because pancreas isn’t having enough blood supply
- Lungs problem such as difficult in breathing
- Pancreatic pseudocyst, due to fluid collection in pancreas
Symptoms of Pancreatic Disorders
Pancreatic disorders signs and symptoms vary, there are some general symptoms that may indicate pancreatic disorders, listed below:-
- Pain in upper abdominal pain that goes back
- Severe abdominal pain after having food
- Upset stomach and vomiting
- Fever
- Rapid heart beat
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Unwanted weight loss
- Stinking and oily stool
- Diarrhea
- Tender and swollen belly
- Dehydration
- Bleeding
- Pancreatitis; which is more likely to occur in people with diabetes
Common Disorders of the Pancreas
There are a different type of disorders related to the pancreas including acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, hereditary pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis occurs suddenly; causing inflammation of the pancreas and and is a short-term condition. Common cause for acute pancreatitis:-
- Gallbladder stone (40% cases of acute pancreatitis)
- Moderate or heavy alcohol consumption (25% cases of acute pancreatitis)
- Hereditary conditions
- Hormonal abnormalities
Severe abdominal pain, tender and swollen belly, diarrhea, nausea, bloating, vomiting and fever are the symptoms of acute pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis may be mild and can develop further complications if not treated and monitored properly, such as:
- Pancreas infection
- Necrotizing pancreatitis
- Pancreatic pseudocyst
- Organ failure
Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is long-term inflammation of the pancreas. It is a progressive disorder associated with the damaging the tissues of the pancreas that can't be reversed. It is more common in male aged between 32 to 45 years. Initially symptoms of the chronic and acute pancreatitis are similar such as severe abdominal pain, tender and swollen belly, diarrhea, nausea, bloating, vomiting and fever. In chronic pancreatitis patient can develop malabsorption, malnutrition and unwanted weight loss.
Chronic pancreatitis is long-term progressive disease; causing permanent damage of the pancreas. Common cause for chronic pancreatitis:-
- Heavy alcohol consumption and Smoking
- Recurrent acute pancreatitis
- Cystic fibrosis
- Gallbladder stone
- Hereditary conditions
- High triglycerides
- Medications
Hereditary Pancreatitis
Hereditary pancreatitis is a rare genetic condition occur due to recurrent pancreatic attacks, which can lead to chronic pancreatitis. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, tender and swollen belly, diarrhea, nausea, bloating, vomiting and fever.
It also increase lifetime risk of pancreatic cancer. Hereditary pancreatitis can't be cured completely, can be managed by medical management, pancreatic enzyme supplements to cope-up with maldigestion, insulin for diabetes, medications to control pain and lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer
Smoking and alcohol consumption can increase the risk for pancreatic attacks. It is strongly recommended to quit smoking and drinking alcohol.
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer occur when uncontrolled cell growth begins in the tissues of the pancreas. Cancerous and noncancerous tumors growths can occur in the pancreas. Pancreatic cancer can be cured if detected early but in most of the cases due to no symptoms is early stages its difficult to find it.
Pancreatic cancer can also slow down the production of digestive enzymes by the pancreas, resulting in difficulty to break down food and absorbing nutrients. This mal-absorption causes bloating, watery, greasy, foul-smelling stool, further can lead to weight loss and vitamin deficiencies.
Smoking and alcohol consumption can increase the risk for pancreatic attacks. It is strongly recommended to quit smoking and drinking alcohol.
Diagnosing Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis has physical findings that affect body systems including Pain in upper abdominal pain that goes back, severe abdominal pain after having food, upset stomach and vomiting, fever, rapid heart beat, nausea and Vomiting, unwanted weight loss, stinking and oily stool, diarrhea, tender and swollen belly, dehydration, bleeding.
Pancreatitis treatment depends on stage and its cause. It’s very important to find the cause and extent of pancreas damage in guiding treatment.
Diagnosing Pancreatitis:
Depending on symptoms, we will ask about medical history, any family history of pancreatitis, drinking and eating habits, taking any prescription or over-the-counter medications, including vitamins and supplements. To diagnose pancreatitis, we may recommend:
- Blood and Stool tests: Amylase or lipase blood test and Stool routine test for digestive enzymes of the pancreas. It will be elvated 3 times in pancreatitis from its normal range. If blood test is showing normal ranges then we need to go futher evaluation.
- Imaging tests: To understand pancreatitis and figure out what’s the cause. We may recommend:
1. X-rays with a barium meal
2. Ultrasound imaging: specifically evaluate the gallbladder for stones - Endoscopic ultrasound: It is a type of endoscopic examination to evaluate pancreatic masses and tumors, pancreatic cysts, small stone in bile duct and gall bladder not identified during ultrasound. This procedure is perfomed to collect small tissues of pancreas using FNA needle through the wall of the stomach or intestine directly into the pancreas.
- CT Scan, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), or PET scans : types on non-invasive tests for detailed imaging of the pancreas and the surrounding. CT scans expose the patient to some amount of radiation. Furthermore, some patients are unable to receive IV contrast for their CT scans (due to allergies or kidney problems), and thus the quality of the pictures will be sub-optimal. A special kind of MRI called an MRCP can give high-quality pictures of the pancreas, the pancreas duct, and the bile ducts. However, some patients who are claustrophobic may decide against having an MRI performed.
- Biopsy or Tissue analysis: We will remove a tissue sample (biopsy) from pancreas may help diagnose pancreatitis and further look for signs of pancreatitis.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): to view the bile duct and pancreatic duct. It helps to remove gallstones from the bile duct gallstones that are causing a blockage.
Pancreatitis treatment depends upon its cause. It’s very important to find the cause and extent of pancreas damage in guiding treatment.
Treatment of Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis treatment usually require short-term or long-term hospitalization to intiate the aggressive treatment.
Antibiotics , if pancreas is infected
Intravenous (IV) fluids, it helps to prevent dehydration so that the rest of the organs of the body get adequate blood flow to support the healing process.
Low-fat diet or fasting , to stop eating so your pancreas can recover. In this case, nutrition will be given through a feeding tube.
Pain medicine
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): to take out gallstones if they’re blocking your bile or pancreatic ducts. There different procedures that can be performed using ERCP like:
- Sphincterotomy for pseudocyst drainage
- Gallstone removal
- Stent placement: placing a tiny piece of plastic or metal that looks like a straw into a narrowed pancreatic or bile duct to keep it open.
- Balloon dilatation: to dilate, or stretch, a narrowed pancreatic or bile duct to keep the duct open
Gallbladder surgery if gallstones caused your pancreatitis
Pancreas surgery such as
- Whipple procedure
- Distal pancreatectomy
- Total pancreatectomy to clean out fluid or dead or diseased tissue a liver transplant.