Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammation of digestive or GI (gastrointestinal) tract. The digestive tract includes mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine. The important function to break down food, nutrients extraction and removing any unused material and waste from the items we intake. Prolonged digestive or GI (gastrointestinal) tract inflammation can damage digestive or GI (gastrointestinal) tract.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) are different from each other. Although symptoms are similar.
Bloating, on and off stomach pain, gas, diarrhea, blood in stool, weight loss due to malabsorption, anemia due to malnutrition are the initial symptoms of the Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Types of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
There are three major types of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD):
- Crohn's disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Indeterminate colitis
Its always important to understand the types before starting treatment for any of these three types of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) - Crohn's disease, Ulcerative colitis and Indeterminate Colitis. Crohn's diseases, Ulcerative colitis and Indeterminate Colitis these three are chronic disease.
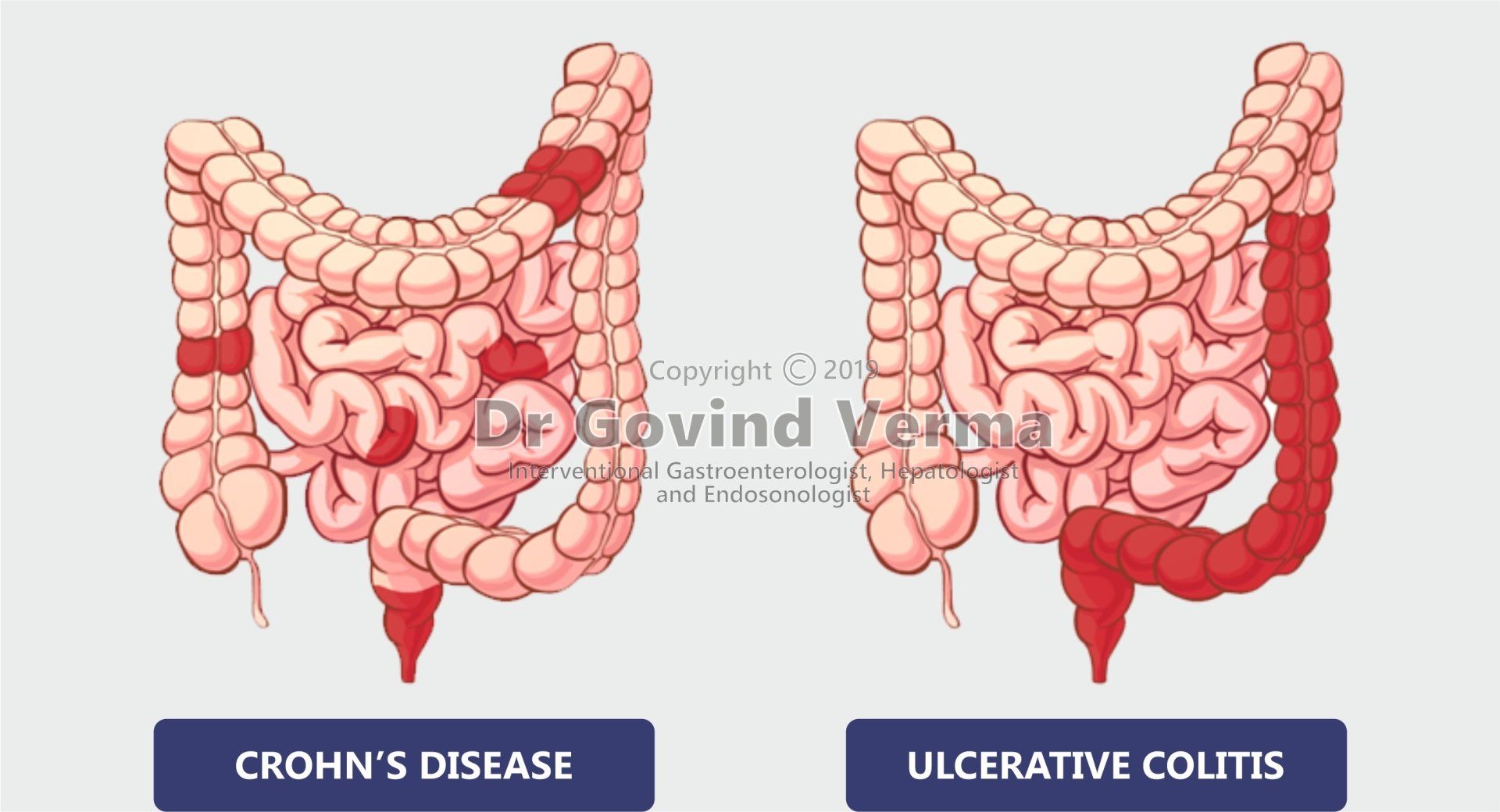
- Crohn's disease affect any where in the gastrointestinal tract. It may not be limited to the only gastrointestinal (GI) tract (simultaneously will be affecting the liver, skin, eyes, and joints).
- Ulcerative colitis (UC) only affects the lining of the large intestine. Men and women both are affected equally.
- Indeterminate Colitis (IC) is used when there is symptom and some form of IBD is present. Based on the research 10 to 15% in IBD case might be suffering with IC.
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease can cause inflammation to any part of the digestive or GI (gastrointestinal) tract - starting from mouth to anal canal - although majorly affecting the portion of the small intestine and the colon. The actual cause of Crohn's disease is still its not clear. Your immune system, heredity and enviornment are the factors that can influence this. The symptoms may be varing, it depends on which part of the stomach is affected and severity of this. Patients might notice
- Diarrhea (bloody and containing mucus or pus)
- Unwanted Weight loss
- Fever
- Pain in abdomen and tenderness
- Abdomen Fullness
Ulcerative colitis (UC)
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is type of an inflammatory bowel disease that causes chronic and long duration inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract majorly large intestine. Ulcerative colitis causes ulcers on the inner lining of the large intestine, inflammation and irritation. As per research and study; ulcerative colitis (UC) patients will be having inflammation and ulcers of the inner lining of the large intestine and colon that will be leading to diarrhea, abdominal pain and bleeding.
Ulcerative colitis is a long term disease, usually patients have symtoms on and off, it start gradually and can go worse in long time.
Indeterminate Colitis (IC)
Indeterminate Colitis (IC) is term used when there is symptom and some form of IBD is present. Based on the research 10 to 15% in IBD case might be suffering with IC.
The distinction between ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) has major implications, including the choice of medical treatment, timing of surgery, prognosis, and disease course. In addition, there is a need for surveillance in UC, and possibly also in Crohn’s colitis, because it may have a similar risk to UC. The distinction between UC and CD usually determines whether an ileal pouch anal anastomosis (IPAA) is offered to the patient, and correlates with the occurrence of morbidity and complications from pouch and pouch failure. Because there can be overlapping features of UC and CD in the colons of some patients, the term indeterminate colitis (IC) was coined in an attempt to classify these entities more effectively. Indeterminate colitis continues to be a controversial subject in some circles and might even be considered subjective. Patients with indeterminate colitis appear to have a higher rate of pouch failure and longterm complications than those with UC.
Symptoms of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Pain in abdomen
- Feeling fullness in stomach
- Fever and fatigue
- Unwanted weight loss
- Diarrhea (bloody and containing mucus or pus)
- Mouth ulcers or sores
- Very low appetite
- Anal fissures and rectal bleeding
- Stomach ulcers
Diagnosing Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Blood Test - to find out the anemia and infection
- Stool Test - to rule out the possibility of bacterial, viral, or parasitic causes of diarrhea
- X-rays with barium swallow - abnormality will reflect in film
- CT and MRI Scan - to find out fistulas in the small intestine or anal canal area.
- Colonoscopy
- Upper GI Endosocopy
- Sigmoidoscopy
- Capsule Endoscopy
Treatment of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Stricturoplasty for widening a narrow bowel
- Closing or removing of fistulas
- Removing the affected portions of the intestines, for Crohn’s disease patients
- Removaing the entire colon and rectum, for ulcerative colitis patients