Liver Disorders
Liver is an organ that executes multiple tasks related to metabolism, fights infection, cleans your blood, energy storage, and detoxification of waste. The liver is essential for digesting food, convert it to energy, and store it for your body. Most important; Liver also helps to filter toxic substances. A Healthy Liver can grow back or regenerate when damaged.
Liver disorder or disease is a condition that will be affecting your liver. There are many different types of liver disorders (diseases), these can develop for different reasons, but they can all damage your liver:-
- Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C these diseases caused by viruses
- Fatty liver disease and Liver Cirrhosis, these diseases caused by poisons, drugs, or too much alcohol
- Alcoholic hepatitis caused by drinking too much alcohol
- Wilson disease and Hemochromatosis, these disease are genetic (Inherited)
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) caused by drinking little or no alcohol, obesity, gastric bypass surgery, high cholesterol and type 2 diabetes (based on the research)
- Liver Cancer caused by prolonged Liver malfunctions
Stages of Liver Damage
Symptoms of Liver Disease
Liver disease signs and symptoms vary, there are some general symptoms that may indicate liver disease, listed below:-
- Yellowish skin and eyes (Jaundice)
- Pale stool, bloody or black stool
- Less or Loss of appetite
- Pain in abdomen and swelling
- Legs and ankles swelling
- Extreme tiredness or Feeling exhausted
- Dark urine
- Irritating sensation or Skin problems, such as acne, itching, psoriasis and eczema
- Easy Contusions or Bleeding easily
- Stomach issues after eating, such as bloating, gas, nausea and vomiting
- Frequently getting headaches, acid reflux & heartburn
- Unexplained weight gain
- severe reaction due to bleach, perfume, paint
Some Common Liver Diseases
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a viral infection of liver; identified by 5 unique hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D, and E. It causes inflammation of liver and liver damage, obstructing liver function. Hepatitis viruses are the most common cause of hepatitis in the world but other infections, toxic substances (e.g. alcohol, certain drugs), and autoimmune diseases can also cause hepatitis. Hepatitis is contagious, but risk can be reduced by getting vaccinated for types A and B or taking other preventive steps.
Hepatitis A is most often transmitted through consumption of contaminated water or food. Certain sex practices can also spread.
Hepatitis B spread through infective blood, semen, and other body fluids. Its can be transmitted from infected mothers to infants at the time of birth or from family member to infant in early childhood.
Hepatitis C is mostly transmitted through exposure to infective blood. This may happen through transfusions of HCV-contaminated blood and blood products, contaminated injections during medical procedures, and through injection drug use.
Hepatitis D is a serious form of hepatitis that only develops in people with hepatitis B — it can’t be contracted on its own.
Hepatitis E is usually caused by consumption of contaminated water or food.It is increasingly recognized as an important cause of disease in
developed countries
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease happens due to moderate or heavy alcohol consumption. There are 3 types of alcoholic liver disease -
- Alcoholic Cirrhosis
- Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
The signs and symptoms for each of these more or less are same. Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes), Fatigue, Low-grade fever, Loss of appetite, Nausea, Vomiting, Tenderness in upper abdomen, Weight loss and Digestive issues are the most common symptoms of alcoholic liver disease.
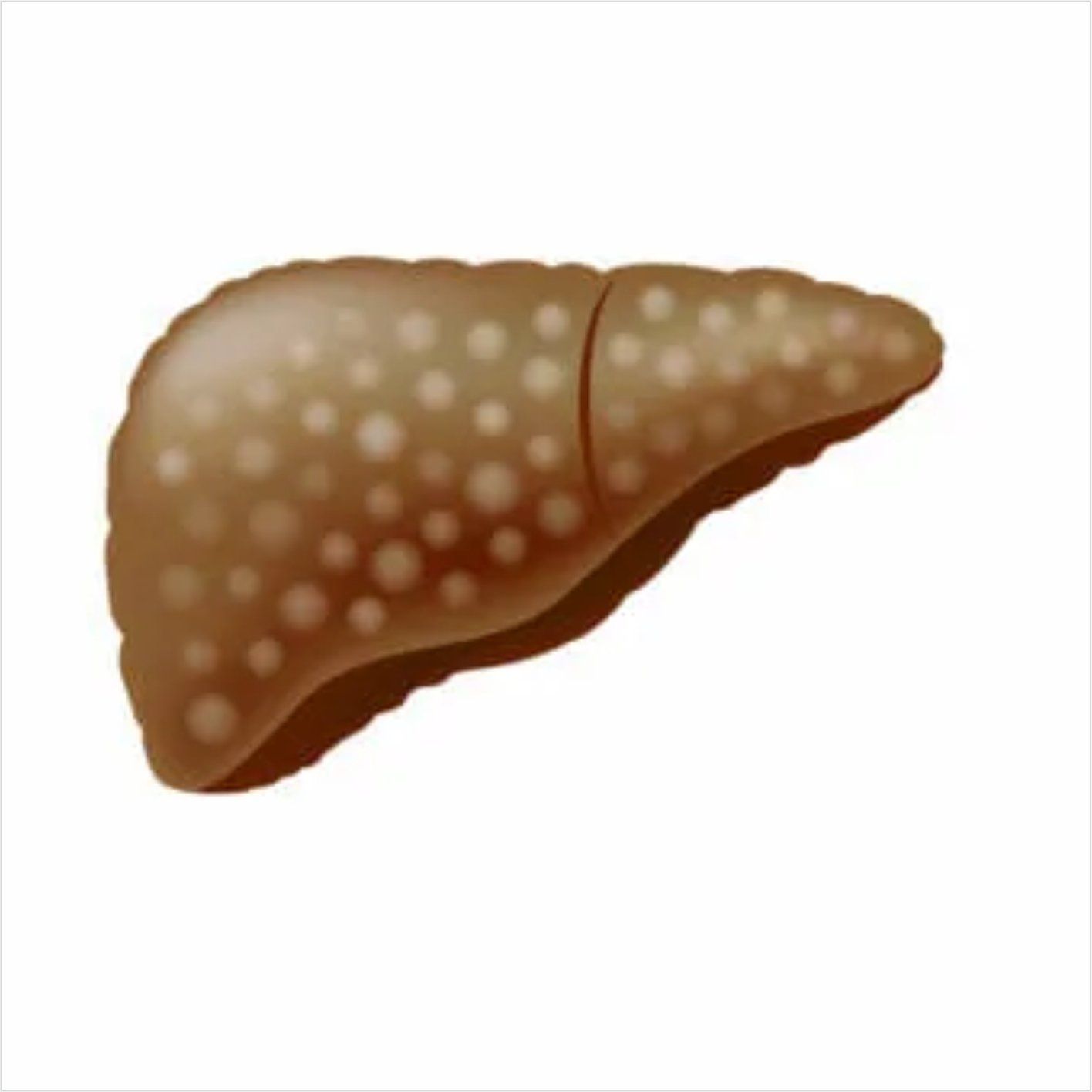
Fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease happens due to extra fat builds up in the liver which can lead to liver damage, liver scarring or cirrhosis.
Fatty liver disease is more common in people who have type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes, obesity, middle aged or older (although children can also get it), high levels of fats in the blood (cholesterol and triglycerides), high blood pressure, certain metabolic disorders (metabolic syndrome), sudden weight loss, certain infections (hepatitis C). It is also known as hepatic steatosis.
There are mainly two types of Fatty liver disease, Non-alcoholic and Alcoholic.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) occurs when fat builds up in the liver who don’t drink a lot of alcohol or not at all drinking alcohol.
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP)
is a type of NAFLD and a serious pregnancy complication. Researchers found it in the third trimester of pregnancy, cause still unknown.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) or Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) or Alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH) occurs when drinking a lot of alcohol, due to this liver will be inflamed and could be tender.If not treated in early stage it can cause scarring of liver. Heavy liver scarring is known as cirrhosis and further can lead to liver failure.
Genetic Liver Disease
An abnormal gene transferred from one or both of your parents can cause various substances to build up in your liver, resulting in liver damage.
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson's disease
- Alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency
Autoimmune Liver Disease
Autoimmune liver disease occurs when your immune system mistakes and turns against liver tissues. The exact cause of autoimmune liver disease is unknown, researchers found genetic and environmental factors are the main cause of Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). If not treated in early stages this can lead to scarring liver tissues can result cirrhosis and further liver failure. Autoimmune liver disease can be treated with drugs when diagnosed in early stages.
Liver specialist has identified two types of Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH):-
- Type 1 - Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)
- Type 2 - Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)
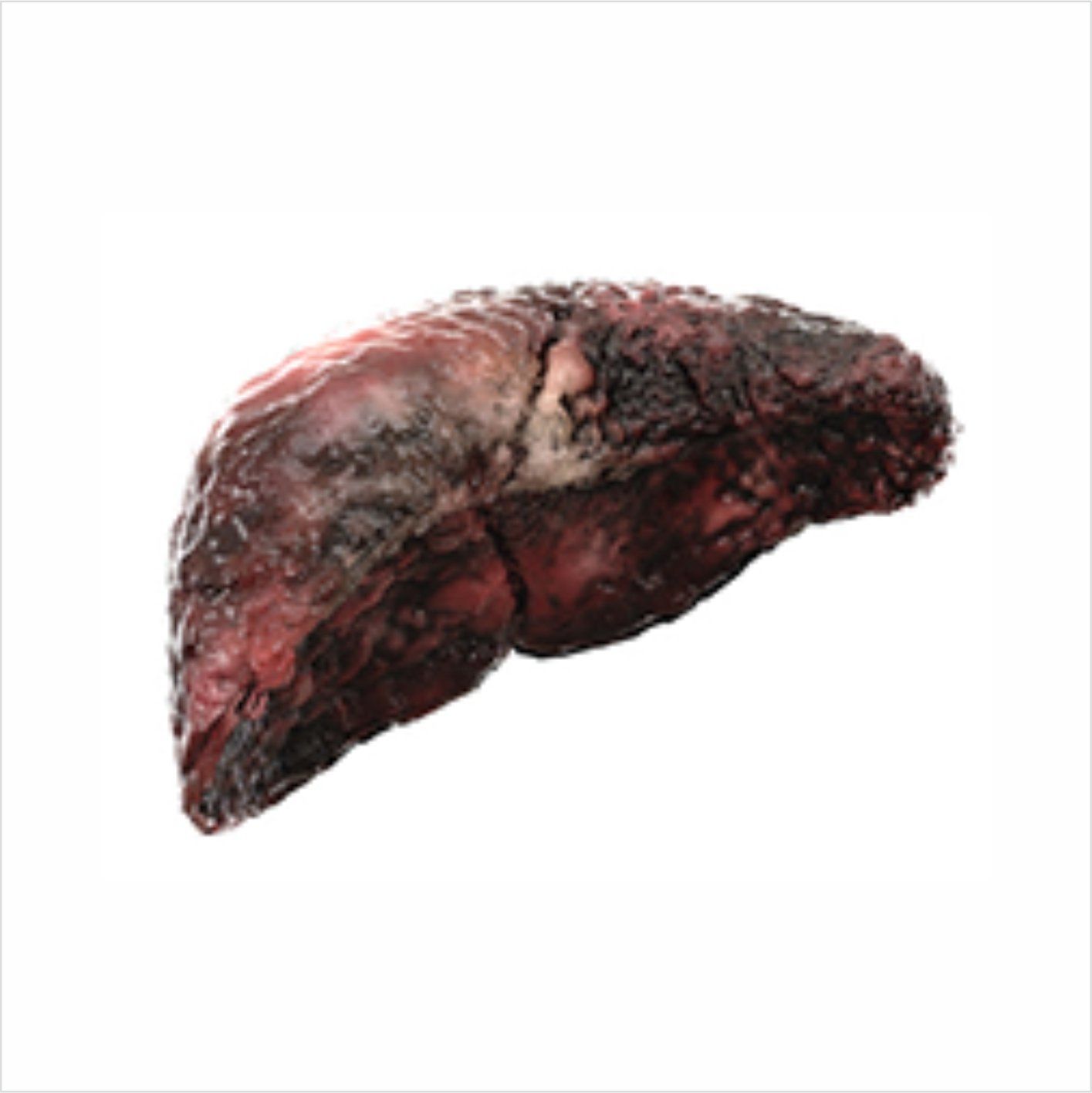
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis in stage 3 Liver disease, caused by so many forms and conditions including hepatitis, fatty liver disease (NAFLD, AFLD), genetic liver disease, virus infection and many more. Liver damage cant be revered in cirrhosis but can be treated when diagnosed early, further damage can be controlled but can't reverse this.
Liver Cancer and Failure
Liver Cancer and failure is last stage of liver disease it occurs due to long term liver malfunction and when not treated in early stages. When liver tissues damage, it form tumor in liver and further affect liver functions. Liver cancer can't be cured if not detected in early stages. Its very important to regular follow up and medication as advised.
Types of Liver Disease
Treatment of Liver Disease
Liver disorders (diseases) have physical findings that affect body systems including the heart, lungs, abdomen, skin, brain and cognitive function, and other parts of the nervous system.
Liver disease treatment depends on stage and its cause. Many liver diseases are chronic, they can last for years. Even chronic liver diseases can usually be managed. It’s very important to find the cause and extent of liver damage in guiding treatment.
Diagnosing Liver Disease:
Depending on symptoms, we will ask about medical history, any family history of liver problems, drinking and eating habits, taking any prescription or over-the-counter medications, including vitamins and supplements. Once we’ve collected all these information, we may recommend:
- Blood tests: Liver function tests can be used to diagnose liver disease. Other blood tests can be done to look for specific liver problems or genetic conditions. Prothrombin time test, which measures how long it takes your blood to clot, due to acute liver failure, blood doesn't clot as quickly as it should.
- Imaging tests: To understand liver damage and figure out what’s the cause. We may recommend - an ultrasound, CT Scan and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Biopsy or Tissue analysis: We will remove a tissue sample (biopsy) from liver may help diagnose liver disease and further look for signs of liver damage.
Liver disorders (diseases) treatment depend on final diagnosis. Some liver problems can be treated with lifestyle changes, such as completely stopping alcohol or weight reduction, typically as part of a follow-up medical program that includes carefully monitoring liver function, diabetes and other affecting diseases. Other liver problems may be treated with medications.
When other options have failed, you may need surgery to remove some part of liver. Liver failure may ultimately require a liver transplant.